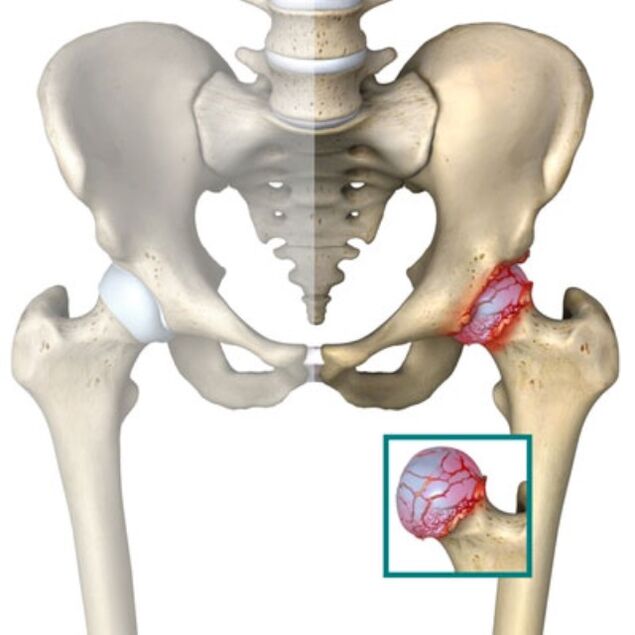
Osteoarthritis of the hip joint is the common name for a group of progressive diseases that include all diseases of the degenerative system of the hip joint, which destroys cartilage tissue. This disease has another name - coxarthrosis. The disease is characterized by pain in the above area and is difficult to treat and diagnose.
Causes and mechanism of development of hip arthrosis
Osteoarthritis of the hip joint is divided into primary and secondary. Primary is a disease that develops independently of other factors, such as side effects of the natural aging process. Secondary osteoarthritis is the result of a complication of a disease of a different nature.
In a healthy pelvis, the distance between the head of the femur and the acetabulum is clearly visible on X-ray. This indicates the optimal condition of the cartilage surrounding the thigh, but also a sign of the absence of osteoarthritis. If the distance is not noticeable, the cartilage is damaged, that is, there is every reason to suspect the existence of the disease described above. This form of osteoarthritis is not genetic, ie it is usually not hereditary. However, factors such as cartilage weakness, bone fragility, and metabolic disorders can contribute to the development of osteoarthritis from generation to generation.
However, the main causes of this disease are various infectious and traumatic diseases. For example:
- Hip dislocation, pelvic dysplasia are the most common congenital diseases diagnosed in early childhood using ultrasound. It is very important to detect this pathology as early as possible, which is present in ten percent of newborns, because the correction of dysplasia is possible only in the first two years of life.
- Infectious and chronic inflammatory diseases such as tuberculosis of the hip joint. This disease is especially dangerous due to its very difficult diagnosis. Often the symptoms are so mild that they are mistaken for another disease. Even radiography can sometimes help diagnose tuberculosis only at an advanced stage, when complete recovery is no longer possible. All this is aggravated by the fact that the country lacks narrow specialists who can correctly diagnose and treat this disease.
- Metabolic and thyroid disorders, such as diabetes mellitus.
- Perthes disease, which affects most boys. The disease affects the femoral head, impairs blood circulation, and as a result suffers from cartilage tissue.
- Various mechanical injuries, such as hip joint injuries and dislocations.
Symptoms
Osteoarthritis is a very dangerous disease because it can be completely asymptomatic at first. Often, only with a good chance, an X-ray examination reveals the presence of the disease in a patient who does not find any symptoms.
Osteoarthritis of the hip joint can be first, second or third degree, depending on the severity of the disease. Primary osteoarthritis is characterized by pain only during physical exertion, such as walking, and only pain in the joint itself. On X-ray, the distance between the head of the femur and the cavity is about half the normal distance. With a secondary disease, the pain intensifies, spreads to the groin, and may even occur at rest, and lameness may appear. The third degree is the most severe, the pain is lasting when the patient is unable to move independently without helpers. Due to the shortening of the leg while walking, a person is forced to bend to one side.
Diagnostics
It is important to collect a correct medical history when making a diagnosis. In this case, first of all, attention is paid to the nature and duration of pain, the location of pain points, atrophy of muscles and nerve endings, the characteristics of the patient's gait, the state of blood circulation in the extremities.
However, X-ray examination is crucial in the diagnosis of osteoarthritis of the hip joint, but additional examinations may be required, such as MRI of the thigh, puncture of the painful area, tomography of the extremities, ultrasound examination.
Treatment of the disease
First of all, in the treatment of osteoarthritis, it is necessary to eliminate the pain or at least reduce it to a level that the patient can tolerate. NSAIDs are used for this, which not only fight pain, but also eliminate inflammation.
Then drugs that nourish the cartilage tissue and are able to restore it are prescribed, but only in the early stages of the disease. If necessary, hormonal injections are also prescribed. However, all of the above medications can only be prescribed by a doctor!
There is the use of physiotherapy (although many experts consider such treatment a waste of time). These are special massage, laser treatment, manual therapy, physiotherapy exercises. However, although these procedures are not a definitive method of treatment, they are also time consuming as a means to the patient.
However, with grade 3 osteoarthritis, doctors generally insist on surgery, while replacing the destroyed joint with a prosthesis.
Folk methods of combating osteoarthritis
Traditional medicine is no exception to the treatment of a serious disease. For this purpose, various ointments and compresses made from maple leaves, burdock, cabbage are used. They are beaten with oatmeal and then tied instead of pain.
A mixture of honey, alcohol, iodine and glycerin is used as compresses. Traditional medicine confirms the effectiveness of baths with nettle decoction. Also, treatment with bee stings has become very popular in getting rid of the disease. Tincture of honey, carrots, beets, radishes and aloe juice should be poured with vodka and infused for a week, after which the tincture can be drunk once a day, 20 grams each.
Prevention of coxarthrosis
As a rule, preventive measures include strict weight control (because excess weight puts too much strain on the hip joints), proper distribution of physical activity to avoid overloading the joints, and timely contact with a specialist with the slightest suspicion. .
Osteoarthritis of the hip joint is an extremely unpleasant and serious disease that threatens serious complications, but timely consultation with a qualified doctor will help to avoid the terrible consequences of the disease.


















































